What Are Options?
Options are another financial instrument used by investors, day in and day out, to trade on stock and bond markets. Unlike many other tools used by individual and institutional investors, Options have a mechanism by which they operate in a market in relation to economic highs and lows.
An Option is a piece of paper: a contract that gives its holder the right to buy or sell an underlying asset for a particular price till a prescribed date. This means that for Options to function there has to be an underlying asset present against which the contract can be used. Moreover, such a contract does not make it obligatory upon the buyer to exercise his right.
How do they Work?
This stipulation of an Option is very important- and one of the biggest positives that attracts investors. In simple words, if you own an Option, you can choose to use it, trade it, sell it or profit from it provided that market conditions are in your favor. If, on the other hand, they are not favorable, you can choose to do absolutely nothing with the option.
Options expire with time just like a business contract does. The date mentioned on an Option is the expiration date before which, the buyer can exercise his right to the underlying asset. In all other ways, Options are financial securities like bonds, stocks and debentures that are used by investors to strengthen their investment portfolios.
The Option itself has to be bought for a certain dollar amount, which has no connection to the value and worth of the asset that it represents. Therefore, if you choose to let the Option expire because the conditions were such, the only loss to you is the small investment you made to buy the contract. However, if you exercise the Option, the profit made, less this small investment, is your net gain.
While you may have never heard the term Options, you would have come across them in daily life situations for sure. Options are used in every bargain, sale and negotiation. Considering the unpredictable economic conditions worldwide, most industries now use Options to bring a level of certainty to their dealings.
A Classic Options Example
Options and their management is quite different from other financial securities. Because of the nature of this contract, it is hard to grasp all the concepts related to this topic, which is why a daily life example serves as the best way to clarify any confusion you may have. A classic example that is always used to explain how Options work is the purchase of a house.
Lets say you want to buy a house that you really like. The cost of buying is $300,000, an amount that you will have two months from now. However, because you do not want to risk the house being sold to another party, you agree to buy an Option from the seller for $4000.
According to the Option, after exactly two months, you can buy the house from the owner for a fixed price of $300,000, even if the market value of the house has soared to $500,000. On the other hand, if you find another property that is even better than this one, you can let the Option expire. In this case, your loss will be $4000 that you paid to buy the contract.
Types of Options
There are two types of Options:
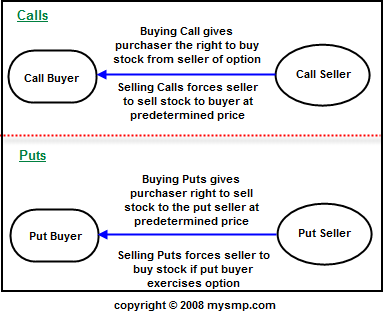
- Call Option– A Call Option gives the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at a particular price till the expiration date. So for instance, if you hold a call option for the stocks of a company, you will hope that the price of the stocks rises, so that you still buy at a lower price and earn a profit.
- Put Option– A Put Option is the opposite of a Call Option. It gives the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at a particular price till the expiration date. So for instance, if you hold a put option for the stocks of a company, you will hope that the price of the stocks falls, so that you can sell the stocks at a higher price than their market value.
Source: Mysmp.com
Why Trade Options?
Options offer various benefits to the investors that include leveraged exposure, more return, and protection for portfolios with long equity positions. The options are a kind of hedging strategy that protects the investors portfolio during market crisis. Another great advantage of trading options is the leverage that comes with the trade; a single option controls a hundred shares of an underlying security. However, despite all the advantages, the option trading carries substantial risks, which is why many financial strategists recommend investing in option only with the risk capital.
Option Strategies
Options offer various opportunities for the investors to alter a portfolio. The best option strategy is to invest in an all options portfolio. This strategy produces great leverage, which makes it very risky, but at the same time, substantially profitable.
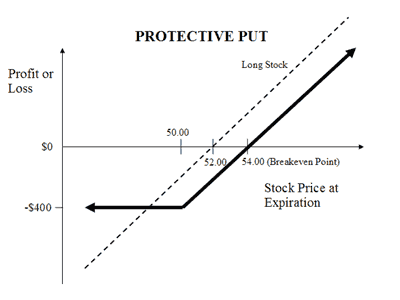
Protective put strategy is a great example of the option strategy where an investor purchases a put on portfolio or stock with the price of the put less than the market value of the underlying security or asset.
Source: The Options Guide
This strategy keeps the investment secure as the lowest value of the protective put strategy is the exercise value of the put.
As described by The Options Guide, Protective put, or Put Hedge is a strategy where the holder of a security buys a put to guard against a drop in the stock price of that security.
The features of Protective Put strategy are as follows:
- Unlimited Profit Potential
- Limited Risk :
Max Loss = Premium Paid+Purchase Price of Underlying – Put Strike +Commissions Paid
- Breakeven Point
BE Point = Purchase Price of Underlying + Premium Paid
There are other similar bullish strategies with limited risk and unlimited profit potential, like Married put, Call Backspread and Long Call Option strategies.
HedgeThink.com is the fund industry’s leading news, research and analysis source for individual and institutional accredited investors and professionals