Can Twitter and Google predict the stock markets? The European Central Bank – ECB research thinks and rightly so considers it !
A recent research study was carried out in July 2015 by Huina Mao, Scott Counts and Johan Bollen for the European Central Bank explores the important correlation between Twitter, Google and markets. In these research the authors developed a simple, direct and unambiguous indicator of online and social media investor sentiment that highlights how markets can be partly measured by these social networks – Twitter updates and Google search queries.
Social media and social computation have been having a multi collateral effect in trading and investing. Computational methods and special social media sentiment gauge investor and capital markets sentiment from commonly used online data sources that rely on machine learning classifiers and lexicons, but also social media interactions and search displays have shown considerable promise, but suffer from lack of solid long term research and deeper measurement and classification errors.
“aftermath of the ‘Hack Crash‘ of April 23, 2013, in which markets plummeted after a fake tweet from the Associated Press Twitter account stated that there had been an explosion at the White House. Billions were wiped off the value of stocks, only for the markets to recover strongly a few minutes later when the hoax was revealed. This was the clearest demonstration to date of the power that social media now wields over the capital markets – but also heightened concerns about the use of social media to feed trading strategies, particularly given the growing use of high frequency trading (HFT) strategies to make automated trades.” in TradersDNA Social Media Wielding an Increasing Influence on Markets, According to Survey
From fast growing social media and digital regulation to the episode of the Hack Crash Twitter account that destabilised the world trading markets, there are several episodes of how social media has been disrupting or influencing capital markets and investments. This recent study takes this effect, special in what regards the impact of social media – Twitter and Google – to another level, and it comes more powerful as it comes under the influential umbrella of the European Central Bank.
This Statistics Paper although it should not be reported as representing the views of the European Central Bank (ECB) presents a solid context for illustrating the impact of social media in stock markets as it is sponsor by the bank. The views expressed are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the ECB but indeed solidifies the relation and the gravity.
Overall the study carried out research which looked at indicators of online investor feelings based on Twitter and Google effect in investors and markets. This recent research attempts further to discuss the links between Twitter and Google and the stock markets.
This was based on Twitter updates and Google search queries that had been made. The goal of the study was to investigate new investor bullishness on international stock markets considering the role of Google and Twitter. The sutyd can be found in this PDF here: Quantifying the effects of online bullishness on international financial markets

Twitter bullishness predicts changes in Google bullishness
Overall, the study found that changes in Twitter bullishness predicts changes in Google bullishness. This in turn suggests that Twitter information drives Google queries that are made. A second finding was that Twitter and Google bullishness were both found to be related to investor feeling and lead established investor sentiment surveys.
In particular, Twitter was found to be very important in predicting changes in sentiment in the stock market. This was much more the case than for Google. Yet another finding was that high Twitter bullishness predicts increases in stock returns, rather than returning to fundamental values. This was found to potentially “support the investor sentiment hypothesis in behavioural science.”
The way that the study was carried out with regard to the gathering of the Twitter data, tweets were assessed as being bullish if they included the word “bullish” and bearish if they included the word “bearish”. The data was collected over a time period between 2010 and 2012, and during this time frame it was identified that there were 0.31 million bullish and bearish tweets.
What this meant was that there were 280 bullish and bearish tweets in total and these were posted across 1,091 days. The study identified that there was a clear weekly pattern of bullish and bearish tweet volume. Specifically there were high volumes on trading days. There were also peaks on Tuesdays and Thursdays. Weekend days had lower tweets of this nature, attributed to the lack of trading on those days.
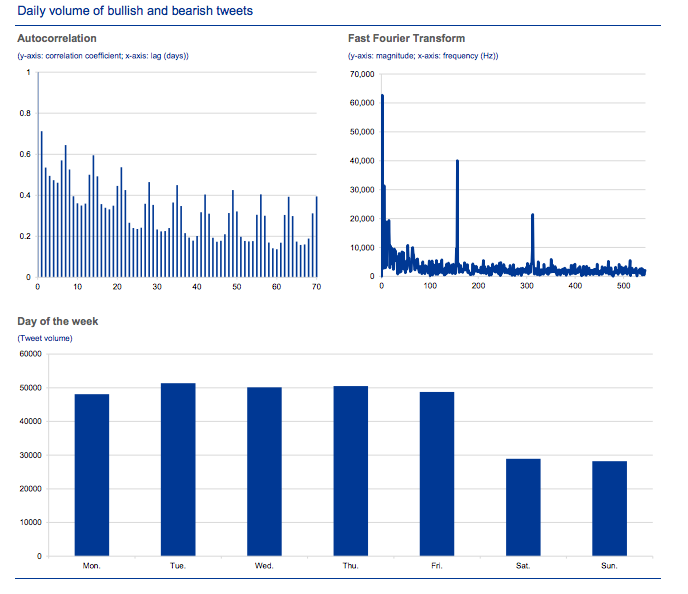
The distribution of bullish or bearish tweets paires with investor behaviour
This finding was found to be similar to other studies that had been carried out. It could be seen from this that the distribution of bullish or bearish tweets paired with investor behaviour. As well, the ratio of bullish tweets to total bullish and bearish tweets was 69.4%, and this was taken to mean that one of two things was happening. The first was an optimistic bias of online investors, and the second was the Pollyanna effect. The Pollyanna effect is explained to be that humans like positive words more than negative ones.
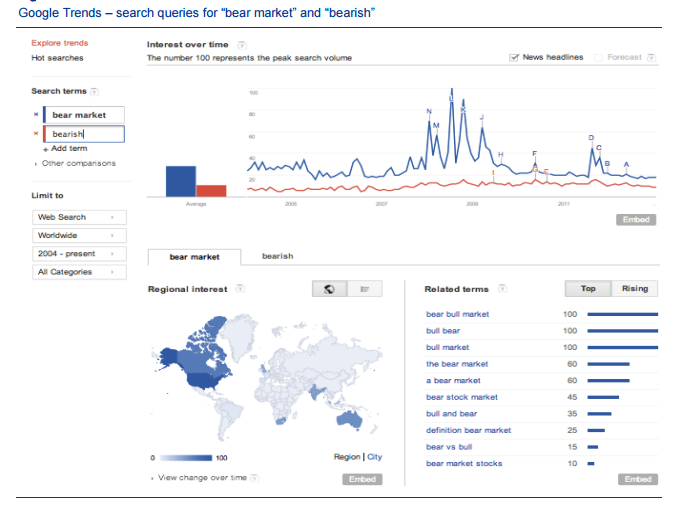
Turning to the Google data, Google bullishness was extrapolated from the number of Google searches that included the aforementioned financial terms. The tool Google Trends was used to establish the number of searches that had been made. It was seen in this case that the volumes of Google queries using adjectives “bullish” and “bearish” were low, and this relates to people’s search behaviour. People do not commonly search for adjectives. For this reason the adjectives were switched for “bull market” and “bear market”.
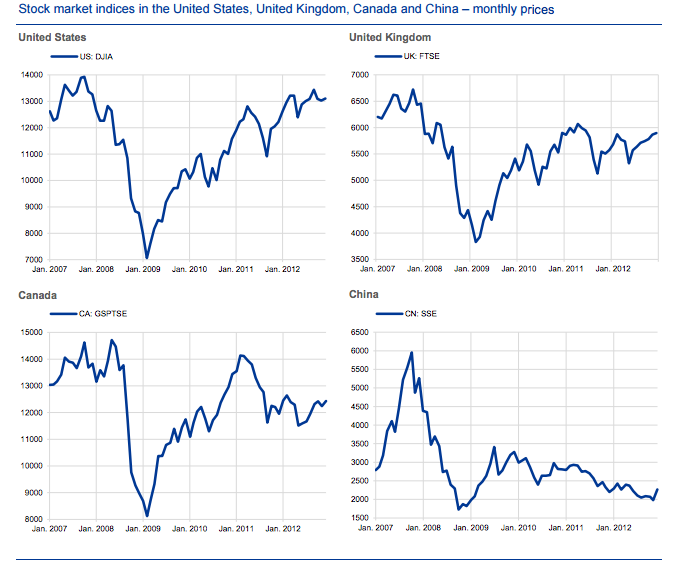
The study carried out in four different countries, namely the United Kingdom, the USA, China and Canada
The study was carried out in four different countries, namely the United Kingdom, the USA, China and Canada. The idea of using several countries was to make sure that the results would be valid. Three of the countries (the USA, the UK and Canada) were selected because many people use both Twitter and Google in these countries.
China was included for the fact that various aspects of its financial markets are so different to the other three countries. In particular the investor behaviour, market structure and legal system are very different. Also the use of social media and search engines is very different. Overall, the inclusion of China added greater diversity to the study.
This study highlights the emergence of the digital economy, special the impact of Twitter and Google, as a disruptive empowerment of a new generation of investors with advanced market tools, that offers new big data and additional trading elements and sentiment dashboards at their fingertips. These investors will have to begin to select investments based not only on their personal interests, but will have to go the extra mile to use real time tools to learn and understand what markets and investors sentiments are more relevant for their investments and trading operations, rather than cash flow and income statements.
In short, this study highlights how software (now social media real time big data) is eating the investment world.
“(…) we are in the middle of a dramatic and broad technological and economic shift in which software companies are poised to take over large swathes of the economy. “Marc Andreessen, WSJ
New finance and the emergence of Fintech new technologies and accessible social media and big data, social media investment and markets real time data platforms together with the growth and credibility of peer to peer funding, and Crowdfunding developed an alternative new way of looking at the investment. An investment that is macro and idea-real-time-based investing. Twitter and Google are the first mainstream digital players opening doors to a new world of investing and trading that is no longer black and white but full of computational and algorithm based social media data processed, both by machines and humans in parallel.
In Part 2 of “Can Twitter and Google Predict the Stock Markets?” we will look at the lead-lag relationship between Twitter and Google bullishness. We will also look in greater depth at Twitter bullishness and stock market returns as well as Google bullishness and stock market returns, all of which were examined by the European Central Bank in its ground breaking study.
Article written with Paula Newton.
Read More:
hedge fund vs asset management

Dinis Guarda is an author, academic, influencer, serial entrepreneur and leader in 4IR, AI, Fintech, digital transformation and Blockchain. With over two decades of experience in international business, C level positions and digital transformation, Dinis has worked with new tech, cryptocurrencies, drive ICOs, regulation, compliance, legal international processes, and has created a bank, and been involved in the inception of some of the top 100 digital currencies.
Dinis has created various companies such as Ztudium tech platform a digital and blockchain startup that created the software Blockimpact (sold to Glance Technologies Inc) and founder and publisher of intelligenthq.com, hedgethink.com, fashionabc.org and tradersdna.com. Dinis is also the co-founder of techabc and citiesabc, a digital transformation platform to empower, guide and index cities through 4IR based technologies like blockchain, AI, IoT, etc.
He has been working with the likes of UN / UNITAR, UNESCO, European Space Agency, Davos WEF, Philips, Saxo Bank, Mastercard, Barclays and governments all over the world.
He has been a guest lecturer at Copenhagen Business School, Group INSEEC/Monaco University, where he coordinates executive Masters and MBAs.
As an author, Dinis Guarda published the book 4IR: AI, Blockchain, FinTech, IoT, Reinventing a Nation in 2019. His upcoming book, titled 4IR Magna Carta Cities ABC: A tech AI blockchain 4IR Smart Cities Data Research Charter of Liberties for our humanity is due to be published in 2020.
He is ranked as one of the most influential people in Blockchain in the world by Right Relevance as well as being listed in Cointelegraph’s Top People In Blockchain and Rise Global’s The Artificial Intelligence Power 100. He was also listed as one of the 100 B2B Thought Leaders and Influencers to Follow in 2020 by Thinkers360.






































