Today, businesses need to be on top of their game concerning the process improvement which also allows them to give the best in both products and services while consuming the least cost and time. Many such quality enhancements methodologies have gained limelight in reaching the target such as Lean Six Sigma and the advanced version of Six Sigma, the Lean Six Sigma Black Belt. Lean Six Sigma is an approach that combines the two widely recognized management paradigms, i.e. Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma for the purpose of improving business processes, removing waste, and increasing organization efficiency.
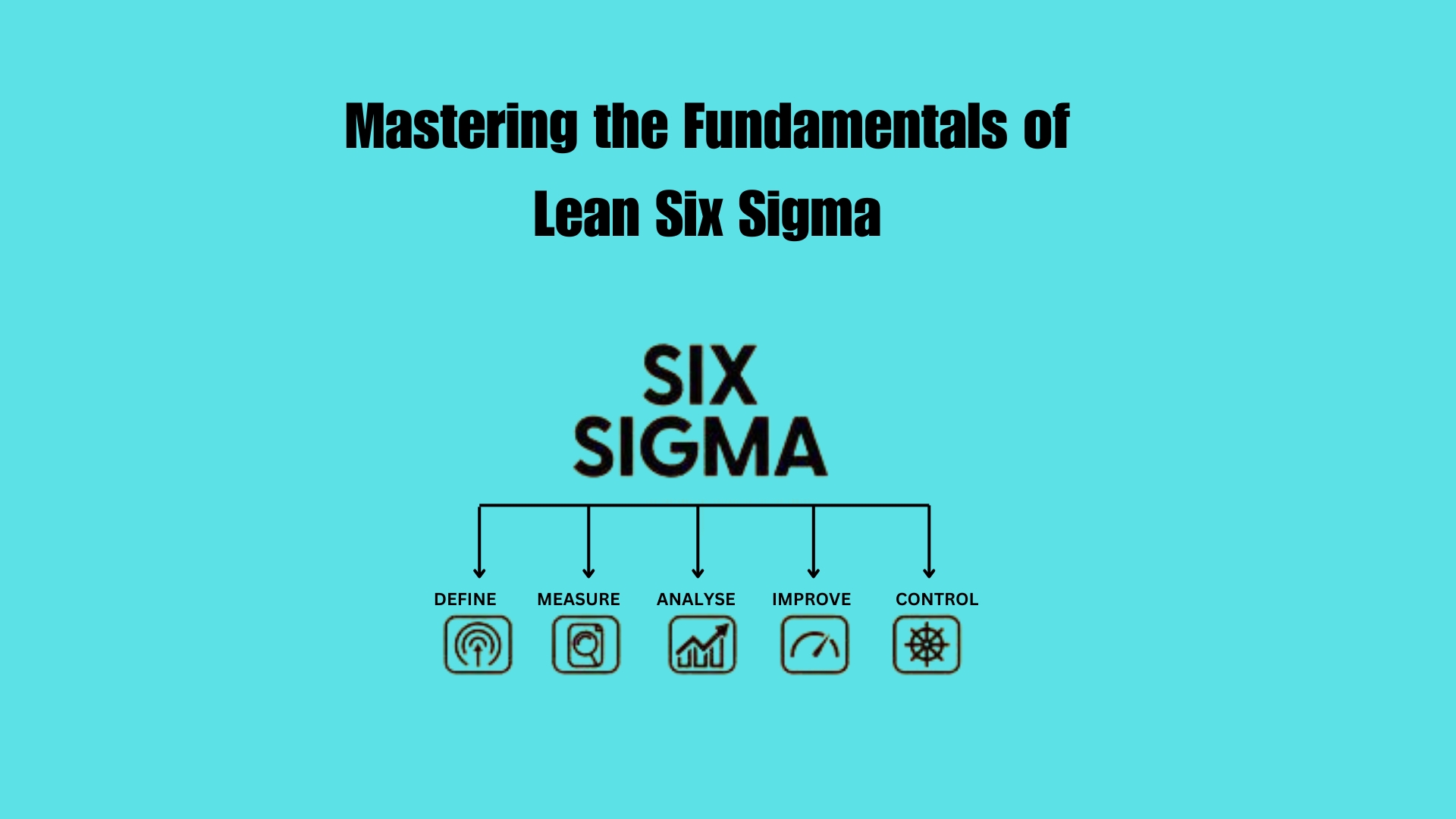
Table of Contents
- Understanding Lean Six Sigma Methodology
- Roles and Responsibilities in Lean Six Sigma
- Benefits of Lean Six Sigma Implementation
- Key Principles of Lean Six Sigma
- DMAIC Methodology
- Challenges in Implementing Lean Six Sigma
- Conclusion
Understanding Lean Six Sigma Methodology
Lean Six Sigma is a methodology that focuses on the monitoring of process variation and eliminating waste in operations. It involves Six Sigma’s main idea – to minimize the amount of defects and to improve the quality of its products – and Lean about getting rid of waste when everything centers around customer value. When this strategy is shelved with these methods, this looks for a rise in overall customer satisfaction, quality, and productivity.
Roles and Responsibilities in Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma implementation process requires the involvement by a specific employee who has definite requests. Leaders become champions and provide leadership and support; Master Black Belts, in turn, manage many projects and mentor Black Belts; Black Belts, in their turn, guide improvement projects; Green Belts assist Black Belts and guide smaller projects; while Yellow Belts, finally, support their field improvement efforts.
Benefits of Lean Six Sigma Implementation
The adoption of Lean Six Sigma offers numerous benefits to organizations, including:
- Improved process efficiency and productivity
- Enhanced product and service quality
- Increased customer satisfaction
- Reduction in costs and waste
- Greater employee engagement and empowerment
- Sustainable competitive advantage
Key Principles of Lean Six Sigma
The fundamental principles of Lean Six Sigma revolve around identifying and eliminating eight types of waste: waste, overproduction, idle time, unused talent, transport, storage, motion, and extra processing. This helps companies make adjustments so that the processes can be improved, and productivity can be improved. Moreover, Lean Six Sigma’s main principle in mind is statistical methods and changes that lead to gradual improvements using systematic problem-solving methods.
- Customer Focus: Lean Six Sigma prioritizes client needs, thereby eliminating all other bottlenecks. Customer needs and wants are key. By orienting all organizational processes this way, they can deliver better value than they have done before.
- Process Optimization: Lean Six Sigma methodology strives to improve processes to the highest possible efficiency and effectiveness. This involves pinpointing bottlenecks, cutting out useless details, and simplifying processes to scrap this extra time and support the company’s survival.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: The primary concept in Lean Six Sigma is the application of statistics to make decisions. By gathering, examining, and decoding data, companies will be able to gain insight into process performance, identify the root causes of issues, and make corresponding decisions to drive improvement.
- Continuous Improvement: The Lean Six Sigma tool is based on a culture of continuous improvement; organizations constantly try to improve their procedures relative to the past. Through a culture of constant education and the forever-abiding mind to develop up-to-date strategies, businesses weather any market conditions and maintain the upper hand over their competitors.
- Employee Involvement and Empowerment: Lean Six Sigma is very focused on company employees’ involvement in the improvement process. By engaging frontline workers in resolving issues and making decisions, organizations can tap their expertise and help create a culture of ownership and accountability.
DMAIC Methodology
At the core of Lean Six Sigma is the DMAIC methodology, which provides a structured approach for process improvement:
- Define: Specify thoroughly the issue, identify the project objectives, and determine the needs and wants of the customers.
- Measure: Make current process inspection, and obtain information related to past performance.
- Analyze: Evaluate the data that may highlight key root causes of problems and the improvement areas.
- Improve: Develop and improve strategies to implement the resolution of listed problems and innovate the processes.
- Control: Develop and put in place measures that will ensure that improvements are sustained, and the situation is not repeated.
Challenges in Implementing Lean Six Sigma
Although Lean Six Sigma can provide many advantages to organizations, this process can also be accompanied by some difficulties. These obstacles are common and include resistance to change, lack of leadership commitment, limited training, and issues of continuous maintenance of the implemented improvements over time. Removing these obstacles depends on the support of top management, successful change management techniques, and ongoing training and development.
Conclusion
Lean Six Sigma is one of those tools that helps to reach control the production processes and improve efficiency to the highest measure. In one way, organizations could eradicate waste, maximize efficiency, and provide more satisfactory services or products to customers when combining Six Sigma methods and Lean principles. It is undeniable that the Lean Six Sigma deployment will cause some certain hassles, but the overall success which brings efficiency improvement, quality enhancement, and customer satisfaction makes the process much more rewarding. Companies can make the most out of Lean Six Sigma in the modern marketplace by developing leaders, providing training, and shifting toward data instrumentation.
I am a writer based in London, specialising in finance, trading, investment, and forex. Aside from the articles and content I write for IntelligentHQ, I also write for euroinvestor.com, and I have also written educational trading and investment guides for various websites including tradingquarter.com. Before specialising in finance, I worked as a writer for various digital marketing firms, specialising in online SEO-friendly content. I grew up in Aberdeen, Scotland, and I have an MA in English Literature from the University of Glasgow and I am a lead musician in a band. You can find me on twitter @pmilne100.



































